Becoming a pediatric doctor is a rewarding career path focused on the health and well-being of children; thebootdoctor.net is here to guide you through every step. This comprehensive guide provides a detailed roadmap, including the educational requirements, training, and certifications necessary to achieve your dream of becoming a pediatrician, as well as information and resources to keep your feet healthy while on your journey. Explore insights into pediatric residency, board certification, and specialized fields like pediatric surgery, alongside practical advice for maintaining foot health throughout your medical career.
1. What Does A Pediatric Doctor Do?
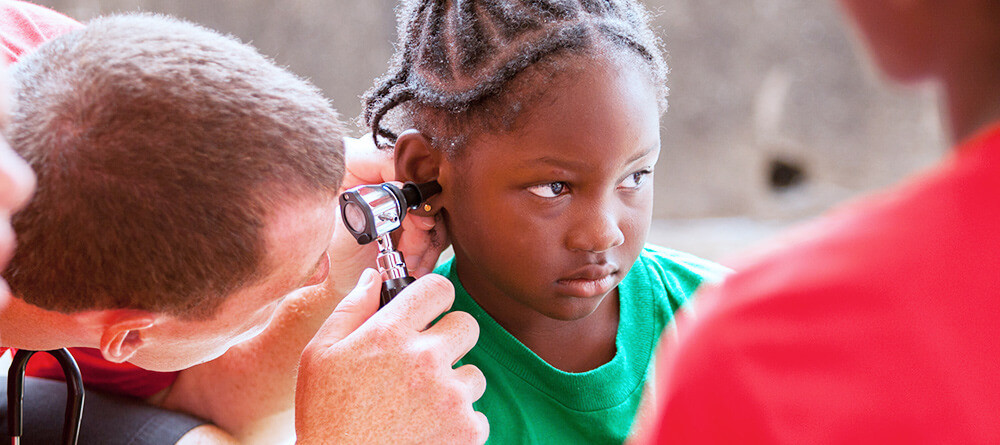
Pediatric doctors, as defined by the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), focus on the mental, physical, and social well-being of children from birth through adolescence. They offer guidance on healthy development and treat various illnesses.
Pediatricians play a vital role in:
- Assessing and Diagnosing: Evaluating children to identify health issues.
- Providing Care: Offering medical treatment and support.
- Supporting Families: Guiding parents in creating a nurturing environment for their children.
Effective communication and empathy are crucial for pediatricians when dealing with children and their families, especially when addressing their fears and anxieties. Pediatricians may work in primary care or specialize in areas like pediatric surgery, collaborating with other healthcare professionals.
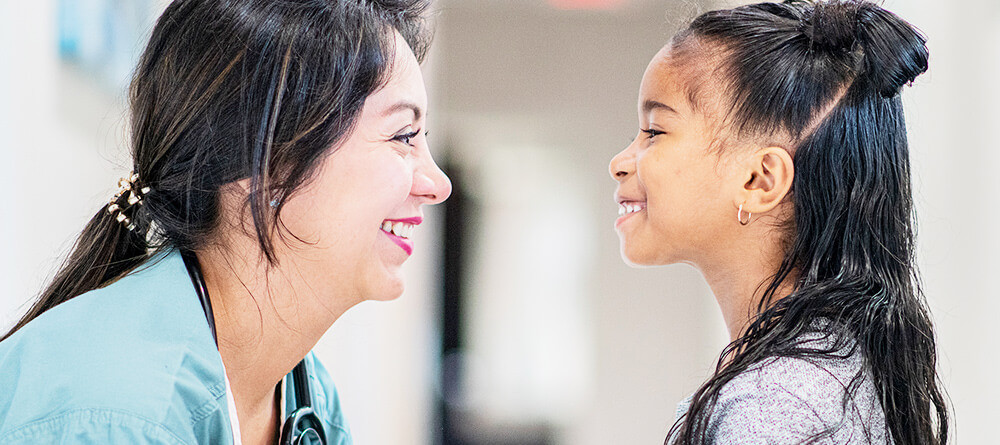 A pediatrician examines a young child during a routine checkup, showcasing the caring interaction between the doctor and patient.
A pediatrician examines a young child during a routine checkup, showcasing the caring interaction between the doctor and patient.
2. What Are The Steps To Becoming A Pediatrician?
The path to becoming a pediatrician involves several steps, typically taking between 7 and 15 years, depending on your chosen path and specialization. thebootdoctor.net is here to help you through the process!
2.1. Earn A Bachelor’s Degree
The first step towards medical school is completing a bachelor’s degree. While there’s no specific major required, excelling in science courses relevant to medical school admissions is beneficial. A strong foundation in sciences is essential for future medical studies.
2.2. Take The MCAT And Apply To Medical School
To get into medical school, preparation for the Medical College Admission Test (MCAT) is essential. Most applicants use services like the American Medical College Application Service (AMCAS) or Canada’s Ontario Medical School Application Service (OMSAS). These applications require transcripts, recommendation letters, and a personal statement.
Medical schools look for core competencies that demonstrate your preparedness for a medical career, including:
- Cultural competence
- Teamwork
- Critical thinking
- Resilience and adaptability
- Scientific inquiry
- Understanding of human behavior
- Ethical responsibility
2.3. Graduate From Medical School
The medical school curriculum includes lectures and lab work in subjects such as anatomy, physiology, biochemistry, and pathology during the first two years. Clinical rotations in the final two years provide direct patient interaction across various specialties like surgery, internal medicine, and pediatrics.
Clinical rotations offer invaluable hands-on experience and help refine your interests within medicine.
 A group of medical students in a classroom setting, participating in a lecture on anatomy, highlighting the academic environment of medical school.
A group of medical students in a classroom setting, participating in a lecture on anatomy, highlighting the academic environment of medical school.
2.4. Complete The Licensure Process
To practice medicine legally in the US, licensure is required, typically fulfilled by completing the three-part United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) series. Starting early is advisable, with Step 1 taken near the end of the second year, Step 2 during the fourth year, and Step 3 during residency.
2.5. Apply For And Complete A Residency
Applying for a pediatric residency position is a crucial step as medical school concludes. A pediatric residency usually lasts three years, but it may extend with further specialization in areas like pediatric cardiology or emergency medicine.
If pediatric surgery is your goal, five years of adult surgery training followed by a two-year fellowship in pediatric surgery will be necessary.
A typical day for a pediatric resident involves:
- Receiving reports from the night team
- Reviewing specific cases
- Making rounds
- Consulting with patients and families
- Performing procedures
- Attending lectures
- Learning from senior doctors
2.6. Get Board Certified
Board certification is achievable after completing a three-year residency program. Although not always mandatory, it signifies a physician’s commitment to exceeding state licensing standards. Pediatricians must pass rigorous exams administered by the American Board of Pediatrics to earn this certification, maintaining it through ongoing continuing education.
For those pursuing pediatric surgery, certification from the American Board of Surgery in both General Surgery and Pediatric Surgery is required.
 A pediatric resident reviewing patient charts in a hospital setting, showcasing the dedication and attention to detail required in pediatric care.
A pediatric resident reviewing patient charts in a hospital setting, showcasing the dedication and attention to detail required in pediatric care.
3. How Long Is Pediatric Residency?
Pediatric residency typically lasts three years, but additional training may be required for those specializing in a specific area. According to the American Board of Pediatrics, residency programs must provide a well-rounded experience in general pediatrics and its subspecialties.
4. What Are The Different Pediatric Subspecialties?
Pediatrics has numerous subspecialties, allowing doctors to focus on specific areas of child health. Each subspecialty requires additional fellowship training after the standard pediatric residency. Here’s a table that summarizes the various pediatric subspecialties, including a brief description and the typical length of fellowship required:
| Subspecialty | Description | Fellowship Length (Years) |
|---|---|---|
| Adolescent Medicine | Focuses on the unique health needs of adolescents. | 2-3 |
| Pediatric Cardiology | Specializes in heart conditions in children. | 3 |
| Child Abuse Pediatrics | Deals with the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of child abuse and neglect. | 2-3 |
| Pediatric Critical Care | Manages critically ill children in intensive care units. | 2-3 |
| Developmental-Behavioral Pediatrics | Focuses on developmental and behavioral issues in children. | 3 |
| Pediatric Emergency Medicine | Provides emergency care for children. | 2-3 |
| Pediatric Endocrinology | Treats hormonal and metabolic disorders in children. | 3 |
| Pediatric Gastroenterology | Manages digestive system disorders in children. | 3 |
| Pediatric Hematology-Oncology | Treats blood disorders and cancers in children. | 3 |
| Pediatric Infectious Diseases | Specializes in infectious diseases affecting children. | 3 |
| Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine | Cares for premature and newborn infants. | 3 |
| Pediatric Nephrology | Treats kidney disorders in children. | 3 |
| Pediatric Pulmonology | Manages respiratory diseases in children. | 3 |
| Pediatric Rheumatology | Treats autoimmune and inflammatory conditions in children. | 2-3 |
| Pediatric Sports Medicine | Focuses on the treatment and prevention of sports-related injuries in children. | 1-2 |
5. How Many Years Of Schooling For A Pediatrician Are Required?
The educational path to becoming a pediatrician is extensive, typically requiring 11 to 15 years of schooling and training post-high school. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
- Bachelor’s Degree: 4 years
- Medical School: 4 years
- Pediatric Residency: 3 years
- Fellowship (optional for specialization): 1-3 years
6. What Is The Job Outlook For Pediatricians?
The job outlook for pediatricians is promising. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, employment of physicians and surgeons is projected to grow 3% from 2022 to 2032, about as fast as the average for all occupations. About 27,200 openings for physicians and surgeons are projected each year, on average, over the decade. All of those openings are expected to result from the need to replace workers who retire or transfer to other occupations.
Factors contributing to this positive outlook include:
- Growing population: Increased demand for healthcare services for children.
- Advances in medical technology: Improved treatment options and preventive care.
- Increased access to healthcare: More families seeking pediatric care.
7. What Is The Average Pediatrician Salary?
The salary of a pediatrician can vary based on location, experience, and specialization. According to recent data, the average pediatrician salary in the United States is around $200,000 to $250,000 per year. Factors such as practice setting (private practice, hospital, or clinic) and geographic location can influence earnings.
Here’s a table that illustrates the range of salaries for pediatricians based on experience level:
| Experience Level | Average Annual Salary |
|---|---|
| Entry-Level | $180,000 – $220,000 |
| Mid-Career | $230,000 – $270,000 |
| Experienced | $280,000 – $350,000+ |
8. How To Choose The Right Medical School?
Choosing the right medical school is a critical step in your journey to becoming a pediatrician. Here are several factors to consider when making your decision:
- Accreditation: Ensure the medical school is accredited by a recognized body, such as the Liaison Committee on Medical Education (LCME) in the US or the Committee on Accreditation of Canadian Medical Schools (CACMS) in Canada.
- Curriculum: Look for a curriculum that provides a strong foundation in basic sciences and clinical skills, with opportunities for early clinical exposure.
- Location: Consider the location of the medical school and whether it aligns with your personal and professional preferences.
- Faculty: Research the faculty members and their expertise in pediatrics and related fields.
- Research Opportunities: If you are interested in research, look for medical schools with robust research programs and opportunities for student involvement.
- Residency Match Rates: Check the medical school’s residency match rates, particularly in pediatrics, as this can indicate the quality of training and preparation students receive.
- Financial Aid and Scholarships: Explore the financial aid and scholarship options available at each medical school to help offset the cost of tuition and living expenses.
- Campus Culture: Visit the campus and speak with current students to get a sense of the campus culture and whether it is a good fit for you.
9. What Are The Challenges Of Being A Pediatrician?
While being a pediatrician is incredibly rewarding, it also comes with its unique set of challenges. Understanding these challenges can help you prepare for the realities of the profession. Some of the common challenges include:
- Emotional Toll: Dealing with sick or injured children can be emotionally challenging, especially in severe cases.
- Long Hours: Pediatricians often work long and irregular hours, including nights, weekends, and holidays, particularly during residency.
- Parental Expectations: Managing parental expectations and addressing their concerns can be demanding, as parents are often anxious and protective of their children.
- Ethical Dilemmas: Pediatricians may face ethical dilemmas, such as end-of-life decisions or conflicts between parental wishes and the best interests of the child.
- Administrative Burden: Like all physicians, pediatricians must navigate the complexities of healthcare administration, including paperwork, billing, and insurance regulations.
- Keeping Up with Advances: The field of pediatrics is constantly evolving, so pediatricians must stay current with the latest research, guidelines, and treatments.
- Burnout: The combination of emotional stress, long hours, and administrative burden can lead to burnout if not properly managed.
10. What Is The Importance Of Foot Health For Medical Professionals?
Maintaining foot health is crucial for medical professionals, especially pediatricians, who spend long hours on their feet. thebootdoctor.net emphasizes the importance of proper foot care to prevent common issues and ensure overall well-being.
10.1. Common Foot Problems
- Plantar Fasciitis: Inflammation of the plantar fascia, causing heel pain.
- Bunions: Bony bumps at the base of the big toe.
- Blisters: Fluid-filled pockets caused by friction.
- Athlete’s Foot: Fungal infection causing itching and burning.
10.2. Tips For Maintaining Foot Health
- Wear Comfortable Shoes: Choose supportive footwear with good cushioning.
- Use Orthotics: Consider custom orthotics for added support and alignment.
- Stretch Regularly: Perform foot and calf stretches to improve flexibility.
- Keep Feet Clean and Dry: Wash feet daily and dry thoroughly to prevent infections.
- Change Socks Daily: Wear moisture-wicking socks to keep feet dry.
10.3. Recommended Footwear Brands
Choosing the right footwear can make a significant difference in preventing foot problems. thebootdoctor.net recommends brands known for their support and comfort.
- Hoka One One: Known for their maximum cushioning and stability.
- Brooks: Offers a range of supportive running shoes suitable for long hours on your feet.
- Dansko: Popular among healthcare professionals for their all-day comfort and support.
- New Balance: Provides a variety of shoes with excellent arch support and cushioning.
11. What Are The Key Skills For A Successful Pediatrician?
To excel as a pediatrician, a combination of medical knowledge, technical skills, and interpersonal abilities is essential. Here are some key skills that contribute to success in this field:
- Medical Expertise: A deep understanding of pediatric medicine, including child development, common illnesses, and treatment options.
- Diagnostic Skills: The ability to accurately diagnose medical conditions based on symptoms, physical exams, and diagnostic tests.
- Communication Skills: Effective communication with children, parents, and other healthcare professionals.
- Empathy: The ability to understand and share the feelings of patients and their families.
- Patience: A calm and patient demeanor when dealing with children who may be scared or uncooperative.
- Problem-Solving Skills: The ability to think critically and solve complex medical problems.
- Decision-Making Skills: The ability to make sound medical decisions under pressure.
- Organizational Skills: Effective time management and organizational skills to manage a busy practice.
- Teamwork: The ability to work collaboratively with other healthcare professionals as part of a multidisciplinary team.
- Adaptability: The ability to adapt to changing situations and new medical advancements.
12. What Are The Current Trends In Pediatrics?
The field of pediatrics is continually evolving, with new trends and advancements shaping the way care is delivered. Staying informed about these trends is essential for providing the best possible care to young patients. Some of the current trends in pediatrics include:
- Telehealth: The use of technology to provide remote healthcare services, including virtual consultations and monitoring.
- Preventive Care: An increased focus on preventive care and early intervention to promote lifelong health.
- Mental Health: Greater attention to mental health issues in children and adolescents, including anxiety, depression, and ADHD.
- Vaccination: Ongoing efforts to promote vaccination and address vaccine hesitancy.
- Obesity Prevention: Strategies to prevent and manage childhood obesity through diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes.
- Precision Medicine: The use of genetic information to tailor treatment plans to individual patients.
- Integrated Care: Collaboration between pediatricians and other specialists to provide comprehensive care for children with complex medical needs.
- Advocacy: Pediatricians advocating for policies and programs that support child health and well-being.
13. How Does Technology Impact Pediatric Care?
Technology is transforming the landscape of pediatric care, offering new tools and opportunities to improve patient outcomes and enhance the delivery of healthcare services. Some of the ways technology is impacting pediatric care include:
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): EHRs streamline documentation, improve communication, and facilitate data analysis for quality improvement.
- Telemedicine: Telemedicine allows pediatricians to provide remote consultations, monitor patients, and offer support to families in underserved areas.
- Mobile Apps: Mobile apps provide parents with access to valuable information, resources, and tools for managing their children’s health.
- Wearable Devices: Wearable devices monitor vital signs, track activity levels, and provide real-time data to pediatricians for remote patient monitoring.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being used to analyze medical images, predict patient outcomes, and assist with clinical decision-making.
- Virtual Reality (VR): VR is being used to create immersive experiences for children during medical procedures and to provide therapeutic interventions for conditions like anxiety and autism.
- 3D Printing: 3D printing is being used to create custom prosthetics, medical models, and surgical guides for pediatric patients.
14. How To Balance Work And Life As A Pediatrician?
Balancing work and life as a pediatrician can be challenging due to the demanding nature of the profession. However, it is essential for maintaining your well-being and preventing burnout. Here are some strategies for achieving a healthy work-life balance:
- Set Boundaries: Establish clear boundaries between work and personal time and stick to them as much as possible.
- Prioritize Self-Care: Make time for activities that help you relax, recharge, and maintain your physical and mental health.
- Delegate Tasks: Delegate tasks to other members of your healthcare team to reduce your workload.
- Seek Support: Lean on your colleagues, friends, and family for support and understanding.
- Time Management: Use effective time management techniques to maximize your productivity and efficiency.
- Vacation Time: Take regular vacations and breaks to disconnect from work and recharge.
- Hobbies and Interests: Pursue hobbies and interests outside of medicine to add variety and fulfillment to your life.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practice mindfulness and meditation to reduce stress and improve your overall well-being.
15. What Is The Role Of Research In Pediatrics?
Research plays a crucial role in advancing the field of pediatrics and improving the health and well-being of children. Pediatric research encompasses a wide range of areas, including:
- Clinical Trials: Evaluating new treatments, therapies, and interventions for pediatric medical conditions.
- Epidemiological Studies: Investigating the patterns and causes of diseases in children.
- Basic Science Research: Exploring the fundamental mechanisms of child health and development.
- Health Services Research: Examining the effectiveness and efficiency of healthcare delivery systems for children.
- Translational Research: Bridging the gap between basic science discoveries and clinical applications in pediatrics.
- Outcomes Research: Assessing the impact of medical interventions and healthcare policies on child health outcomes.
- Quality Improvement Research: Identifying and implementing strategies to improve the quality and safety of pediatric care.
Research findings inform clinical practice, guide healthcare policies, and contribute to the development of new treatments and preventive measures for childhood illnesses.
FAQ: Becoming A Pediatrician
-
How many years does it take to become a pediatrician?
It typically takes 11 to 15 years after high school, including a bachelor’s degree, medical school, and residency. -
Is being a pediatrician stressful?
Yes, it can be stressful due to long hours, emotional challenges, and the need to stay updated with medical advancements. -
What is the hardest part of being a pediatrician?
Dealing with seriously ill children and managing parental expectations are often cited as the most challenging aspects. -
What are the benefits of being a pediatrician?
The rewards include making a positive impact on children’s lives, continuous learning, and opportunities for specialization. -
What is the job outlook for pediatricians?
The job outlook is positive, with a projected growth in employment driven by increasing demand for healthcare services. -
Do pediatricians have good work-life balance?
Maintaining work-life balance can be challenging but is achievable with effective time management and self-care strategies. -
What skills are important for a pediatrician?
Key skills include medical expertise, communication, empathy, problem-solving, and decision-making. -
What are the different subspecialties in pediatrics?
Subspecialties include cardiology, emergency medicine, endocrinology, gastroenterology, and hematology-oncology, among others. -
How can I prepare for medical school as an undergraduate?
Focus on excelling in science courses, gaining clinical experience, and participating in extracurricular activities. -
What is the role of a pediatrician in preventive care?
Pediatricians play a crucial role in preventive care by providing vaccinations, health screenings, and guidance on healthy lifestyles.
The path to becoming a pediatrician is challenging but immensely rewarding. With dedication, perseverance, and the right resources, you can achieve your dream of caring for children and making a positive impact on their lives. Remember to prioritize your foot health along the way, ensuring you can continue to provide the best possible care.
If you’re looking for more information on foot health, treatment options, or expert advice, visit thebootdoctor.net. Our resources can help you stay informed and maintain healthy feet throughout your medical career. Contact us today for personalized recommendations and support. Address: 6565 Fannin St, Houston, TX 77030, United States. Phone: +1 (713) 791-1414. Website: thebootdoctor.net.
