Are you dealing with a bothersome bump on your eyelid and wondering, “Do Eye Doctors Treat Styes?” The answer is yes, eye doctors, including ophthalmologists and optometrists, absolutely treat styes, and at thebootdoctor.net, we want to ensure you receive the best information and care for your eye health. This article will explore how eye doctors diagnose and treat styes, offering solutions and preventive measures to keep your eyes healthy and comfortable. You’ll also learn about related conditions like chalazia, blepharitis, and how to maintain proper eyelid hygiene.
1. What is a Stye?
A stye, also known as a hordeolum, is a painful, red bump that forms on the eyelid, typically caused by a bacterial infection. According to the American Academy of Ophthalmology, styes usually develop when oil glands in the eyelid become blocked and infected. This infection is commonly caused by bacteria, often Staphylococcus aureus.
- External Styes: These form on the outside of the eyelid and are usually caused by an infection of an eyelash follicle or an oil gland.
- Internal Styes: These develop inside the eyelid and are typically caused by an infection of the meibomian glands, which produce oil that helps lubricate the eye.
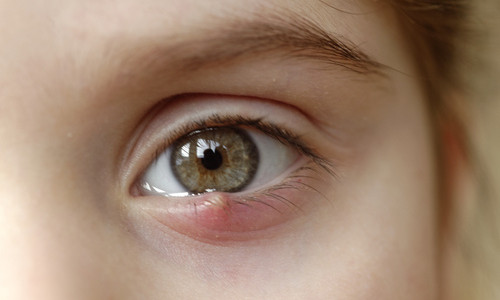 Close-up of an eye with a stye on the upper eyelid, showing redness and swelling
Close-up of an eye with a stye on the upper eyelid, showing redness and swelling
Symptoms of a Stye
- Redness: The area around the stye becomes red and inflamed.
- Swelling: The eyelid swells, causing discomfort.
- Pain: Styes can be painful, especially when touched.
- Tenderness: The affected area is usually tender to the touch.
- Crusting: A crust may form around the eyelid.
- Tearing: Increased tear production in the affected eye.
- Gritty Sensation: A feeling that something is in the eye.
- Sensitivity to Light: Also known as photophobia.
- Blurred Vision: In rare cases, a large stye can press on the cornea, causing temporary blurred vision.
2. Can Eye Doctors Treat Styes Effectively?
Yes, eye doctors are equipped to treat styes effectively through various methods. According to a report by the Mayo Clinic, most styes resolve on their own with simple home care, but if a stye persists or worsens, professional treatment from an eye doctor may be necessary.
- Diagnosis: Eye doctors can accurately diagnose a stye through a comprehensive eye examination.
- Treatment Options: They offer treatments ranging from prescription medications to minor surgical procedures.
- Prevention Advice: Eye doctors provide valuable advice on preventing future styes and maintaining overall eye health.
3. When Should I See an Eye Doctor for a Stye?
Knowing when to seek professional help is crucial for managing styes effectively. According to the American Academy of Ophthalmology, you should see an eye doctor if:
- The stye doesn’t improve after a week of home treatment: If warm compresses and over-the-counter remedies don’t alleviate the symptoms, it’s time to consult a professional.
- The stye affects your vision: Any changes in vision warrant immediate attention from an eye doctor.
- The stye is extremely painful: Severe pain could indicate a more serious infection.
- The stye bleeds or oozes pus: These symptoms may require prescription medication or drainage.
- The swelling spreads to other parts of your face: This could indicate a more widespread infection.
- You have a fever: A fever accompanied by a stye could signify a systemic infection.
4. What Treatments Do Eye Doctors Offer for Styes?
Eye doctors offer a range of treatments for styes, tailored to the severity and specific characteristics of the condition. These treatments aim to alleviate symptoms, eradicate the infection, and prevent recurrence.
- Antibiotic Ointments: Prescription antibiotic ointments, such as erythromycin or bacitracin, can effectively combat bacterial infections.
- Antibiotic Eye Drops: For styes accompanied by conjunctivitis or other surface infections, antibiotic eye drops like ciprofloxacin or ofloxacin may be prescribed.
- Oral Antibiotics: In cases of severe or recurrent styes, oral antibiotics such as doxycycline or azithromycin might be necessary to address the infection systemically.
- Incision and Drainage: If a stye doesn’t respond to medication or is particularly large and painful, the eye doctor may perform a minor surgical procedure to drain the pus. This involves making a small incision in the stye and gently expressing the contents.
- Steroid Injections: In some instances, steroid injections may be administered to reduce inflammation and swelling associated with the stye.
5. How Can I Treat a Stye at Home Before Seeing a Doctor?
Many styes can be effectively managed at home with simple remedies. The American Academy of Ophthalmology recommends the following:
- Warm Compresses: Apply a warm compress to the affected eyelid for 10-15 minutes, 3-4 times a day. This helps to open the oil glands and promote drainage.
- Eyelid Hygiene: Gently clean the eyelid with a mild, diluted soap (like baby shampoo) or eyelid wipes to remove debris and bacteria.
- Avoid Makeup: Refrain from wearing eye makeup until the stye has healed to prevent further irritation and infection.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relief: Use over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen to manage pain and discomfort.
- Saline Solution: Rinse the eye with a sterile saline solution to keep it clean and prevent further infection.
- Tea Bags: Apply a warm, moist tea bag (such as chamomile or green tea) to the eyelid for its anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties.
- Avoid Contact Lenses: If you wear contact lenses, switch to glasses until the stye has healed to avoid contamination and irritation.
- Gentle Massage: Gently massage the eyelid with clean fingers to help express the blocked oil glands.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to keep your body hydrated and support overall eye health.
- Rest: Get adequate sleep to allow your body to heal and recover.
6. What is the Difference Between a Stye and a Chalazion?
It’s essential to distinguish between a stye and a chalazion, as they are often confused but have different characteristics and treatments. According to the Mayo Clinic, a stye is an acute infection, while a chalazion is a chronic inflammation.
Stye (Hordeolum)
- Nature: An acute, painful bacterial infection of the oil glands or eyelash follicles.
- Symptoms: Redness, swelling, pain, and pus formation on the eyelid.
- Cause: Usually caused by Staphylococcus aureus bacteria.
- Location: Occurs on the edge or inside the eyelid.
- Progression: Develops rapidly and is typically painful.
- Treatment: Often resolves with warm compresses, antibiotic ointments, and sometimes drainage.
Chalazion
- Nature: A chronic, non-infectious inflammation of the meibomian gland.
- Symptoms: A painless, slow-growing bump on the eyelid.
- Cause: Blockage of the meibomian gland, leading to oil accumulation.
- Location: Occurs deeper within the eyelid tissue.
- Progression: Develops slowly and is typically painless unless it becomes large and presses on the cornea.
- Treatment: May resolve with warm compresses, but often requires steroid injections or surgical removal.
7. How Can I Prevent Styes?
Preventing styes involves maintaining good hygiene and minimizing risk factors. The American Academy of Ophthalmology offers these preventive measures:
- Wash Hands Frequently: Regularly wash your hands with soap and water, especially before touching your eyes.
- Avoid Touching Your Eyes: Minimize touching your eyes to prevent the transfer of bacteria.
- Proper Contact Lens Care: If you wear contact lenses, clean and disinfect them properly and avoid wearing them overnight.
- Remove Makeup Before Bed: Always remove eye makeup before going to bed to prevent clogged oil glands.
- Use Fresh Makeup: Replace eye makeup regularly to avoid bacterial contamination.
- Avoid Sharing Makeup: Do not share makeup with others to prevent the spread of infections.
- Clean Eyelids Regularly: Gently clean your eyelids with a mild cleanser or eyelid wipes to remove debris and bacteria.
- Manage Blepharitis: If you have blepharitis, follow your eye doctor’s recommendations for managing the condition.
- Balanced Diet: Maintain a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals to support overall eye health.
- Adequate Sleep: Get enough sleep to support your immune system and reduce the risk of infections.
8. What Role Does Blepharitis Play in Stye Development?
Blepharitis, an inflammation of the eyelids, is a significant risk factor for developing styes. According to the American Academy of Ophthalmology, blepharitis can lead to the blockage of oil glands, increasing the likelihood of stye formation.
- Chronic Inflammation: Blepharitis causes chronic inflammation of the eyelids, leading to the buildup of debris and bacteria.
- Gland Blockage: The inflammation can block the meibomian glands, which produce oil that keeps the eyes lubricated.
- Increased Risk: Blocked glands are more susceptible to bacterial infections, increasing the risk of styes.
Managing Blepharitis to Prevent Styes
- Regular Eyelid Hygiene: Clean your eyelids daily with a warm compress and a mild cleanser.
- Warm Compresses: Apply warm compresses to loosen debris and unclog oil glands.
- Eyelid Scrubs: Gently scrub the eyelids with a cotton swab or washcloth soaked in diluted baby shampoo.
- Prescription Medications: Use prescription medications, such as antibiotic ointments or drops, as directed by your eye doctor.
- Omega-3 Supplements: Take omega-3 fatty acid supplements to reduce inflammation and support gland function.
9. What Are the Potential Complications of Untreated Styes?
While most styes resolve on their own or with simple treatment, neglecting them can lead to potential complications. According to the Mayo Clinic, these complications include:
- Chronic Chalazion: An untreated stye can develop into a chronic chalazion, a painless lump that may require surgical removal.
- Preseptal Cellulitis: The infection can spread to the surrounding tissues, causing preseptal cellulitis, a more serious condition requiring oral antibiotics.
- Orbital Cellulitis: In rare cases, the infection can spread deeper into the eye socket, leading to orbital cellulitis, a severe condition that can cause vision loss and requires hospitalization.
- Corneal Damage: A large stye can press on the cornea, causing irritation and potential damage.
- Recurrent Styes: Untreated styes can recur frequently, leading to chronic discomfort and inconvenience.
10. How Can thebootdoctor.net Help Me With My Eye Health?
At thebootdoctor.net, we are committed to providing you with reliable information and resources to maintain optimal eye health. Our website offers:
- Comprehensive Articles: In-depth articles on various eye conditions, treatments, and preventive measures.
- Expert Advice: Guidance from experienced eye care professionals.
- Product Recommendations: Recommendations for effective eyelid cleansers, warm compresses, and other eye care products.
- Find a Doctor: A directory to help you find qualified eye doctors in your area.
- Community Forum: A platform to connect with others, share experiences, and ask questions about eye health.
Contact Information
For personalized advice and treatment options, please contact us:
- Address: 6565 Fannin St, Houston, TX 77030, United States
- Phone: +1 (713) 791-1414
- Website: thebootdoctor.net
By providing expert information and connecting you with qualified professionals, thebootdoctor.net is your trusted partner in maintaining healthy and comfortable eyes.
11. What is the Latest Research on Stye Treatments?
The field of ophthalmology is continuously evolving, with ongoing research exploring new and improved treatments for styes. Recent studies have focused on several key areas, including:
- Advanced Antibiotics: Research is underway to develop more effective topical and oral antibiotics to combat resistant strains of bacteria causing styes.
- Anti-Inflammatory Therapies: Studies are investigating the use of novel anti-inflammatory agents to reduce swelling and discomfort associated with styes.
- Meibomian Gland Dysfunction (MGD) Treatments: Given the link between MGD and styes, research is focusing on treatments such as thermal pulsation and intense pulsed light (IPL) therapy to improve gland function.
- Natural Remedies: Some studies are exploring the efficacy of natural remedies, such as tea tree oil and honey, in treating styes due to their antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties.
Latest Advancements in Stye Treatments
| Treatment | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Pulsation | Uses heat and massage to unclog meibomian glands. | Improves gland function, reduces inflammation, and prevents stye recurrence. |
| Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) | Uses light therapy to reduce inflammation and bacterial load around the eyelids. | Reduces inflammation, kills bacteria, and improves overall eyelid health. |
| Tea Tree Oil | Contains antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties; can be used in diluted form to clean eyelids. | Natural antibacterial and anti-inflammatory agent that can help treat and prevent styes. |
| Manuka Honey | Has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties; can be applied to the eyelid in small amounts. | Natural antibacterial and anti-inflammatory agent that promotes healing. |
| Probiotics | Oral or topical probiotics can help balance the skin microbiome and reduce inflammation. | Supports a healthy skin microbiome, reduces inflammation, and may prevent stye recurrence. |
| Nanoparticle-Based Antibiotics | Uses nanoparticles to deliver antibiotics directly to the site of infection, improving efficacy and reducing side effects. | Enhanced antibiotic delivery, improved efficacy, and reduced side effects. |
| Stem Cell Therapy | Investigating the use of stem cells to regenerate damaged meibomian glands and improve their function. | Potential for long-term improvement in gland function and prevention of styes. |
12. Are There Specific Foods That Can Help Prevent Styes?
While there is no specific diet that can guarantee the prevention of styes, certain foods and nutrients can support overall eye health and reduce inflammation, potentially lowering the risk. These include:
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines), flaxseeds, and walnuts. Omega-3s have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce eyelid inflammation and support gland function.
- Vitamin A: Found in carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach, and kale. Vitamin A is essential for maintaining healthy mucous membranes, which protect the eyes from infection.
- Vitamin C: Found in citrus fruits, berries, and bell peppers. Vitamin C is an antioxidant that supports immune function and helps protect against bacterial infections.
- Vitamin E: Found in almonds, sunflower seeds, and avocado. Vitamin E is another antioxidant that protects cells from damage and supports overall eye health.
- Zinc: Found in oysters, beef, and pumpkin seeds. Zinc is important for immune function and helps the body fight off infections.
- Probiotic-Rich Foods: Found in yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut. Probiotics support a healthy gut microbiome, which can reduce inflammation and improve immune function.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water is crucial for maintaining overall health and keeping the eyes properly hydrated.
13. How Do Contact Lenses Affect Stye Development?
Contact lens wearers are at a higher risk of developing styes due to several factors related to lens handling and hygiene. The American Academy of Ophthalmology advises contact lens wearers to take extra precautions:
- Bacterial Contamination: Contact lenses can harbor bacteria, which can be transferred to the eyes and lead to infection.
- Improper Cleaning: Inadequate cleaning and disinfection of contact lenses can increase the risk of bacterial buildup.
- Overwear: Wearing contact lenses for extended periods, especially overnight, can reduce oxygen flow to the cornea and increase the risk of infection.
- Irritation: Contact lenses can irritate the eyelids, leading to inflammation and blockage of oil glands.
Tips for Contact Lens Wearers to Prevent Styes
- Wash Hands Thoroughly: Always wash your hands with soap and water before handling contact lenses.
- Clean Lenses Properly: Clean and disinfect contact lenses according to your eye doctor’s instructions.
- Replace Lenses Regularly: Replace contact lenses as recommended by your eye doctor.
- Avoid Overwear: Do not wear contact lenses for longer than recommended.
- Use Fresh Solution: Always use fresh contact lens solution and avoid reusing old solution.
- Remove Lenses Before Sleeping: Remove contact lenses before sleeping, unless specifically prescribed for overnight wear.
- Avoid Wearing Lenses When Ill: Avoid wearing contact lenses when you are sick or have an eye infection.
14. What is the Connection Between Stress and Styes?
Stress can indirectly contribute to the development of styes by weakening the immune system and affecting overall health. According to research, chronic stress can suppress the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to bacterial infections.
- Weakened Immune System: Stress hormones like cortisol can suppress the function of immune cells, reducing their ability to fight off infections.
- Poor Hygiene Habits: Stress can lead to poor hygiene habits, such as touching the face and eyes more frequently, increasing the risk of bacterial transfer.
- Inflammation: Chronic stress can promote inflammation throughout the body, including the eyelids, potentially contributing to gland blockage and stye formation.
Managing Stress to Prevent Styes
- Stress Reduction Techniques: Practice stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to reduce stress and boost the immune system.
- Adequate Sleep: Get enough sleep to support immune function and overall health.
- Balanced Diet: Maintain a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals to support immune function and reduce inflammation.
- Self-Care: Prioritize self-care activities that promote relaxation and well-being.
15. FAQ About Styes and Eye Doctor Treatments
1. Can styes spread from one eye to the other?
Yes, styes can spread from one eye to the other if bacteria are transferred through touch. Always wash your hands thoroughly and avoid touching your eyes to prevent the spread of infection.
2. Are styes contagious?
Styes themselves are not contagious, but the bacteria that cause them can spread. Practicing good hygiene can help prevent the spread of bacteria.
3. How long does it take for a stye to heal with treatment from an eye doctor?
With proper treatment, most styes begin to improve within a few days to a week. However, severe or recurrent styes may take longer to heal.
4. Can I wear makeup while treating a stye?
It is best to avoid wearing makeup until the stye has healed to prevent further irritation and infection.
5. What happens if a stye is left untreated?
Untreated styes can lead to complications such as chronic chalazion, preseptal cellulitis, or recurrent styes.
6. Are there any home remedies that can worsen a stye?
Yes, squeezing or attempting to pop a stye can worsen the infection and lead to complications.
7. Can children get styes?
Yes, children can get styes, often due to poor hygiene habits.
8. How often should I clean my eyelids to prevent styes?
Cleaning your eyelids once or twice daily is generally recommended to prevent styes, especially if you have blepharitis.
9. Can certain medications increase the risk of styes?
Certain medications, such as steroids, can weaken the immune system and increase the risk of infections, including styes.
10. Is it possible to develop a stye inside the eyelid?
Yes, styes can develop inside the eyelid, known as internal hordeolum, and may require treatment by an eye doctor.
Conclusion
Dealing with a stye can be uncomfortable, but understanding the causes, treatments, and preventive measures can help you manage the condition effectively. Remember, eye doctors are well-equipped to diagnose and treat styes, providing relief and preventing complications. For reliable information, expert advice, and access to qualified eye care professionals, visit thebootdoctor.net. Prioritize your eye health, and take proactive steps to keep your eyes healthy and comfortable.
