Do Doctors Know When You Fill A Prescription? Yes, doctors can often track if you’ve filled a prescription through various methods like Electronic Health Records (EHRs) and pharmacy communication. At thebootdoctor.net, we aim to provide comprehensive information about medication tracking and its implications for your health and well-being. This process helps ensure patient safety and appropriate medication use, contributing to better healthcare outcomes. Understanding these tracking mechanisms enhances patient awareness and promotes responsible medication management. Let’s delve into the details of prescription monitoring, medication adherence, and electronic prescribing.
1. Electronic Health Records (EHRs): A Comprehensive Overview
What is an EHR and how does it help doctors track prescriptions? An Electronic Health Record (EHR) is a digital record of a patient’s medical information, providing healthcare providers with immediate and secure access to comprehensive patient data. EHRs enhance decision-making, streamline workflows, and improve coordination among healthcare providers.
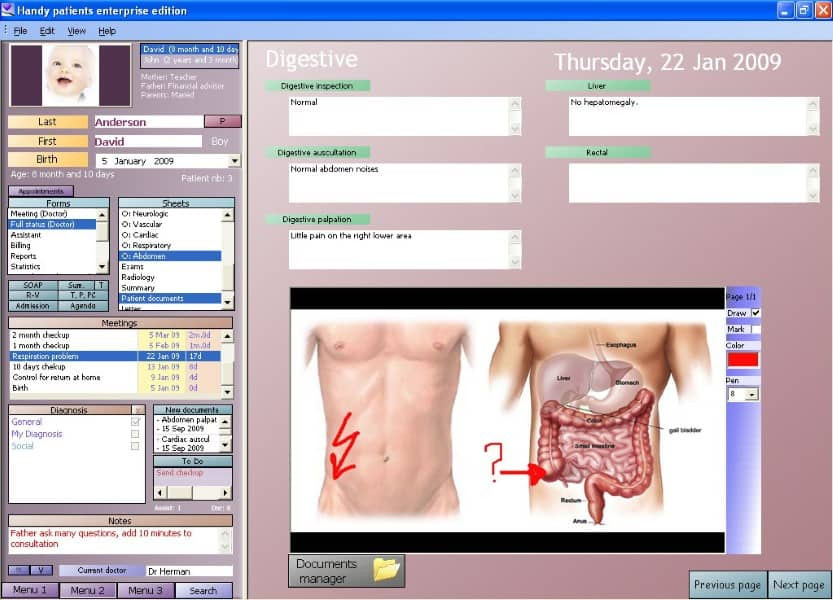 electronic health record
electronic health record
Alt text: Example of an electronic health record interface showing patient data and prescription details
1.1. Key Components of an EHR
What information is typically included in an EHR? An EHR typically includes:
- Treatment plans
- Medications
- Immunizations
- Full medical history
- Diagnoses
- Laboratory and test results
- Allergies
- Radiology images
This comprehensive information enables healthcare providers to make informed decisions about patient care.
1.2. Benefits of EHRs in Tracking Prescriptions
How do EHRs streamline the prescription tracking process? EHRs allow authorized providers to create, manage, and share health information digitally across multiple healthcare organizations. According to HealthIT.gov, a key feature of EHRs is the ability to share information among various providers, including:
- Emergency facilities
- Laboratories
- Specialists
- Medical imagery providers
- Pharmacies
- Work and school medical clinics
This seamless sharing of data helps doctors track whether a patient has filled a prescription.
2. Pharmacy Record Retention Guidelines
How long do pharmacies keep prescription records? Pharmacies maintain records of prescriptions and patient information for specific periods, ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. These guidelines are essential for tracking medication adherence and managing patient care. The following table outlines the retention periods for different types of pharmacy records:
| Record | Description | Retention Period |
|---|---|---|
| Prescriptions | A hard copy record of a prescription | 42 months, or 2 years past the completion of therapy |
| Patient Record | Contains: Demographics, Drug Profile, Record of Care Provided | 10 Years past the last date of Pharmacy Service Provided or 2 years past age of Majority |
| Record of Care | Includes Records of – Drug therapy, problems, interventions & Monitoring | 10 Years past the last date of Pharmacy Service Provided or 2 years past the age of majority |
| Drug Error | Incidents and adverse drug effects, adverse outcomes | 10 years after the error is discovered |
| Health Info Disclosure | Records of diagnosis, treatment, and care. Or records info shared with other health organizations | 10 years following the date of disclosure |
| Narcotic Receipts | Records narcotics received at a pharmacy or licensed outlet, such as a wholesaler | 2 years from the date of the receipt |
2.1. Impact of Pharmacy Records on Medication Tracking
How do these retention guidelines help doctors? These guidelines enable doctors to access historical prescription data, helping them monitor patient adherence and adjust treatment plans accordingly. This information is crucial for ensuring patient safety and optimizing therapeutic outcomes.
3. Electronic Prescriptions (E-Prescriptions)
What are e-prescriptions and how do they aid in medication tracking? Electronic prescriptions (e-prescriptions) allow physicians to send prescriptions directly to a pharmacy electronically, streamlining the process and improving accuracy. This system provides doctors with notifications about whether a prescription has been picked up, not picked up, or partially filled.
3.1. Benefits of E-Prescriptions
Why are e-prescriptions beneficial for both doctors and patients? E-prescriptions offer several advantages:
- Reduced errors
- Improved patient safety
- Enhanced medication adherence
- Streamlined workflow for pharmacies and doctors
The e-Rx program is a valuable tool for doctors to monitor medication adherence and intervene when necessary.
4. Prescription Drug Monitoring Programs (PDMPs)
What are PDMPs and how do they work? Prescription Drug Monitoring Programs (PDMPs) are state-run databases that track the prescribing and dispensing of controlled substances. These programs help identify and prevent drug abuse and diversion.
4.1. How PDMPs Assist Doctors in Tracking Medications
How do PDMPs help prevent drug abuse? More than three dozen states and seven provinces in Canada have established PDMPs to track opioid and narcotic drug prescriptions. These databases monitor:
- Doctors’ prescription-writing habits
- Pharmacy prescription-dispensing practices
- Patients’ prescription-filling activities
When a patient visits a doctor seeking a pain-relieving prescription, the doctor can access the PDMP database to ensure the patient is not “doctor shopping” or amassing more drugs than medically necessary. Discussions are ongoing to enable information sharing across state lines, preventing patients from seeking prescriptions in multiple states.
 doctor prescription
doctor prescription
Alt text: Doctor reviewing a prescription with a patient in an office setting
4.2. Benefits and Concerns About PDMPs
What are the pros and cons of using PDMPs? While some patients are concerned that PDMPs violate their privacy, these programs offer significant benefits:
- Doctors can confidently prescribe drugs to appropriate patients.
- Emergency room personnel can avoid prescribing conflicting medications.
- Patients can be weaned off pain-relieving drugs when appropriate.
Doctors have complete information about their patients’ pain drug history, including prescriptions from other doctors, before establishing a relationship with the patient.
5. Reasons for Medication Non-Adherence
Why do patients sometimes fail to fill their prescriptions? According to the NCBI, approximately 50% of patients do not take their medications as prescribed. Understanding the reasons behind this non-adherence is crucial for improving patient outcomes.
5.1. Common Reasons for Not Filling Prescriptions
What are the most frequent reasons patients don’t adhere to their prescriptions? There are several common reasons:
- Cost: Affordability issues may prevent patients from filling prescriptions.
- Fear: Concerns about potential side effects can deter patients.
- Misunderstanding: Patients may not understand the need for the medication.
- Too many medications: A complex medication regimen can be overwhelming.
- Lack of symptoms: Patients may discontinue medication if they feel their symptoms have disappeared.
- Denial: Patients may believe their condition will resolve on its own.
- Worry: Concerns about dependency can discourage medication use.
- Depression: Depression can lead to a lack of focus on health issues.
- Mistrust: Patients may doubt their doctor’s diagnosis or motives.
5.2. Addressing Patient Concerns
How can doctors address these concerns and improve adherence? Dr. Michael A. Fischer of Brigham and Women’s Hospital advises patients to ask their doctors directly if they are unsure why a medication is being prescribed. Open communication between patients and doctors is essential for ensuring medication adherence.
6. Consequences of Not Filling Prescriptions
What are the potential health and economic impacts of medical non-adherence? Not following a doctor’s advice regarding prescriptions can have far-reaching consequences on both health and the economy.
6.1. Health-Related Consequences
How does non-adherence affect patients’ health? According to a study by The National Council on patient information and education, patients who do not adhere to their medication regimens for long-term diseases like high blood pressure and diabetes are more likely to:
- Be sicker
- Have higher mortality rates
- Suffer more complications
6.2. Economic Consequences
What are the financial implications of non-adherence? The overall cost of medication non-adherence is staggering, amounting to more than $170 billion each year in the United States alone, with some reports estimating the figure as high as $300 billion.
7. Recent Research on Medical Non-Adherence
What new insights have been gained from recent studies on non-adherence? Much of the research on non-adherence has focused on patients who have filled their prescriptions, examining refill patterns and medication adherence. However, recent studies have revealed that non-adherence may begin before a patient even fills their prescription.
7.1. Primary Non-Adherence
What is primary non-adherence and how common is it? Researchers at Harvard Medical School published a study on “primary nonadherence,” finding that more than 20% of first-time patient prescriptions were never filled.
7.2. Factors Influencing Primary Non-Adherence
Which types of prescriptions are most likely to be left unfilled? First-time prescriptions for chronic diseases like high cholesterol, high blood pressure, and diabetes were more likely not to be filled, while those for pediatric patients and antibiotics were more likely to be filled.
 prescription hope
prescription hope
Alt text: Banner advertising prescription assistance programs
8. Strategies to Improve Medication Adherence
What can be done to help patients fill and take their medications as prescribed? Improving medication adherence requires a multifaceted approach involving patients, doctors, and healthcare systems.
8.1. Patient Education
Why is patient education so important? Educating patients about their medications, including their purpose, dosage, and potential side effects, can significantly improve adherence. Doctors should take the time to explain the importance of each medication and address any concerns or misconceptions.
8.2. Simplifying Medication Regimens
How can medication regimens be made easier to follow? Simplifying medication regimens can also enhance adherence. This may involve:
- Combining multiple medications into a single pill
- Reducing the frequency of dosing
- Using medication organizers
8.3. Addressing Financial Barriers
What resources are available to help patients afford their medications? Financial barriers to medication adherence can be addressed through:
- Prescription assistance programs
- Generic medications
- Discounts and coupons
Websites like thebootdoctor.net can provide information about these resources.
8.4. Enhancing Communication
How can better communication improve adherence? Open and ongoing communication between patients and healthcare providers is essential. Patients should feel comfortable discussing any challenges they face in adhering to their medication regimen.
8.5. Utilizing Technology
What role can technology play in improving adherence? Technology can also play a role in improving medication adherence through:
- Medication reminder apps
- Digital pillboxes
- Telehealth consultations
9. Ensuring Data Privacy and Security
How is patient data protected when prescriptions are tracked? Protecting patient data is paramount when tracking prescriptions. Healthcare providers and pharmacies must comply with HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) regulations, which mandate strict privacy and security measures.
9.1. Key HIPAA Provisions
What are the key provisions of HIPAA related to prescription tracking? HIPAA provisions include:
- Limiting access to patient information to authorized personnel
- Using secure electronic transmission methods
- Obtaining patient consent for data sharing
- Implementing safeguards to prevent data breaches
9.2. Maintaining Patient Trust
How can healthcare providers maintain patient trust while tracking prescriptions? Transparency and patient education are essential for maintaining trust. Healthcare providers should explain why they are tracking prescriptions and how the data is being used to improve patient care.
10. The Role of Podiatrists in Medication Management
How do podiatrists contribute to medication management for foot and ankle conditions? Podiatrists, as specialists in foot and ankle care, play a crucial role in medication management for various conditions. They prescribe and monitor medications to treat infections, inflammation, pain, and other foot-related ailments.
10.1. Common Medications Prescribed by Podiatrists
What types of medications do podiatrists commonly prescribe? Common medications prescribed by podiatrists include:
- Antibiotics for infections
- Anti-inflammatory drugs for arthritis and tendonitis
- Pain relievers for acute and chronic pain
- Antifungal medications for fungal infections
- Topical creams and ointments for skin conditions
10.2. Integrating Foot Health into Overall Medication Management
How can podiatrists ensure that foot health is considered in overall medication management? Podiatrists work closely with primary care physicians and other specialists to ensure that medications prescribed for foot conditions do not interact negatively with other medications a patient is taking. This collaborative approach enhances patient safety and optimizes treatment outcomes.
Address: 6565 Fannin St, Houston, TX 77030, United States
Phone: +1 (713) 791-1414
Website: thebootdoctor.net
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Prescription Tracking
Here are some frequently asked questions about prescription tracking:
1. Can my doctor see if I don’t pick up my prescription?
Yes, through EHRs and e-prescription systems, doctors can often see if a prescription has not been picked up.
2. How do PDMPs protect patient privacy?
PDMPs have strict security measures to protect patient data and limit access to authorized personnel.
3. What should I do if I can’t afford my medication?
Talk to your doctor about alternatives, such as generic medications or prescription assistance programs.
4. Are electronic prescriptions more secure than paper prescriptions?
Yes, electronic prescriptions are generally more secure due to reduced risk of fraud and errors.
5. Can my pharmacist see my complete medical history?
Pharmacists can see your prescription history but have limited access to other medical information unless it is shared through an EHR.
6. What are the benefits of using a single pharmacy?
Using a single pharmacy allows the pharmacist to have a complete record of your medications, reducing the risk of drug interactions.
7. How often are PDMPs updated?
PDMPs are typically updated in real-time or daily to provide accurate and timely information.
8. What role does patient education play in medication adherence?
Patient education is crucial for understanding the importance of medications and addressing any concerns or misconceptions.
9. Can my doctor share my prescription information with other healthcare providers?
Yes, with your consent, doctors can share your prescription information with other healthcare providers to coordinate care.
10. What should I do if I experience side effects from my medication?
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience side effects from your medication.
Conclusion
Understanding how doctors track prescriptions is essential for promoting medication adherence and patient safety. From Electronic Health Records and e-prescriptions to Prescription Drug Monitoring Programs, various tools and systems are in place to ensure appropriate medication use. By addressing the reasons for non-adherence and implementing strategies to improve medication management, healthcare providers can enhance patient outcomes and reduce the economic burden of non-adherence.
If you have any questions or concerns about your foot health and medication management, we encourage you to visit thebootdoctor.net. Our comprehensive resources and expert guidance can help you make informed decisions about your care. Contact us today to learn more about how we can assist you in maintaining healthy feet.
