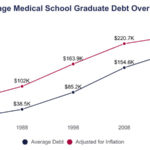
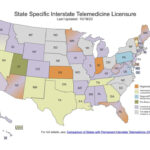
Changing doctors is a significant decision, and understanding the process is essential for your healthcare journey. This guide, brought to you by the experts at thebootdoctor.net, provides a comprehensive overview of how to navigate this process smoothly. Whether you are seeking a new primary care physician (PCP) or a specialist, we are here to ensure you find the right fit for your health needs. You’ll learn about the reasons for changing doctors, steps involved, and how to ensure a seamless transition, all while discovering more about foot health and podiatric care.
1. Why Might You Consider Changing Your Doctor?
There are several reasons why you might want to switch doctors. The best choice depends on your unique demands for medical treatment, so it is crucial to carefully analyze your situation. The most common motivations include:
- Dissatisfaction with Current Care: If you consistently feel unheard or your concerns are dismissed, it might be time for a change. According to a 2023 study by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), patient satisfaction is directly linked to better health outcomes.
- Relocation: Moving to a new city or state often necessitates finding a new healthcare provider.
- Insurance Changes: Your current doctor may no longer be in your insurance network.
- Specialized Needs: You may require a specialist for a specific condition, such as a podiatrist for foot-related issues.
- Communication Issues: Difficulty communicating with your doctor can hinder effective treatment.
- Seeking a Second Opinion: Sometimes, you might want to consult another doctor for a different perspective.
- Changes in Healthcare Needs: As your health needs evolve, your current doctor may not be the best fit.
- Availability and Accessibility: Long wait times or inconvenient office hours can also be reasons to switch.
Changing doctors is a personal decision, and it is essential to prioritize your health and well-being.
2. Understanding Your Health Insurance Plan
Before making any changes, ensure you understand your health insurance plan and its requirements for selecting a primary care provider (PCP). A PCP is your main doctor, who takes care of most of your health needs.
- In-Network vs. Out-of-Network: Check if your preferred doctor is in your insurance network. Seeing an in-network doctor usually means lower out-of-pocket costs.
- Referrals: Some plans require a referral from your PCP to see a specialist.
- PCP Changes: Understand how often you can change your PCP and any associated rules.
- Coverage Details: Review your plan’s coverage for different types of services and treatments.
- Deductibles and Co-pays: Be aware of your deductible and co-pay amounts for doctor visits.
Understanding these aspects of your insurance plan will help you make informed decisions about your healthcare.
3. How to Find a New Doctor
Finding the right doctor involves research and consideration.
- Ask for Recommendations: Seek recommendations from friends, family, or colleagues. Personal referrals can be valuable.
- Online Reviews: Check online reviews on sites like Healthgrades, Vitals, or Zocdoc. These reviews can provide insights into other patients’ experiences.
- Hospital Affiliations: Consider doctors affiliated with reputable hospitals.
- Specialty Boards: Ensure the doctor is board-certified in their specialty.
- Check with Your Insurance: Your insurance provider’s website usually has a directory of in-network doctors.
- Professional Organizations: For specialists like podiatrists, check with professional organizations such as the American Podiatric Medical Association (APMA).
3.1. Finding a Podiatrist
If you are looking for a podiatrist, consider these additional steps:
- APMA Website: The APMA website has a tool to find podiatrists in your area.
- Specialized Clinics: Look for clinics specializing in foot and ankle care, such as thebootdoctor.net.
- Technology and Techniques: Inquire about the technologies and techniques the podiatrist uses, such as laser therapy or minimally invasive surgery.
According to the APMA, the right podiatrist can help you maintain foot health and prevent serious complications.
4. Questions to Ask a Potential New Doctor
Before committing to a new doctor, it is essential to ask the right questions to ensure they meet your needs.
- Are you accepting new patients? This is the most fundamental question.
- What are your office hours and appointment availability? Ensure their hours align with your schedule.
- What insurance plans do you accept? Confirm they are in your network.
- What is your approach to patient care? Understand their philosophy on treatment and prevention.
- How do you handle after-hours or emergency situations? Know their protocol for urgent care.
- What are your qualifications and experience? Verify their credentials and expertise.
- How do you communicate with patients? Do they use email, phone, or a patient portal?
- What is your policy on prescription refills? Understand the process for renewing medications.
- Do you have experience with my specific condition? If you have a particular health issue, ensure they have experience treating it.
- Can I schedule a meet-and-greet appointment? Some doctors offer a brief consultation to get to know you before you become a patient.
These questions will help you make an informed decision and find a doctor who is the right fit for you.
5. Requesting Your Medical Records
Once you have chosen a new doctor, you will need to transfer your medical records. Here is how:
- Contact Your Old Doctor’s Office: Inform them that you are switching doctors and need your records transferred.
- Fill Out a Release Form: Most offices require a signed release form to authorize the transfer of your records.
- Specify the Recipient: Provide the new doctor’s name, address, and contact information.
- Check for Fees: Some offices may charge a fee for copying and sending records.
- Follow Up: Ensure the records have been sent and received by your new doctor.
- Keep a Copy: It is always a good idea to keep a personal copy of your medical records for your reference.
According to the American Medical Association (AMA), patients have a right to access their medical records, so do not hesitate to request them.
6. Informing Your Previous Doctor
While it is not always necessary, informing your previous doctor that you are leaving can be beneficial.
- Professional Courtesy: It is a professional courtesy to inform your doctor of your decision.
- Provide Feedback: You can provide feedback on your experience, which can help them improve their practice.
- Closure: It can provide closure and ensure that there are no loose ends.
- Avoid Assumptions: Informing them directly prevents any misunderstandings or assumptions.
7. What to Do if Your Doctor Leaves Their Practice
Sometimes, doctors leave their practice, which can leave you without a healthcare provider. Here is what to do:
- Check for a Replacement: See if the practice has assigned a new doctor to take over your care.
- Request Your Records: Request your medical records from the practice.
- Find a New Doctor: Start the process of finding a new doctor as soon as possible.
- Contact Your Insurance: Inform your insurance company of the change.
- Temporary Coverage: Inquire about temporary coverage or options for urgent care.
This situation can be stressful, but taking prompt action will ensure you continue to receive the care you need.
8. Tips for a Smooth Transition
To ensure a smooth transition to a new doctor, keep these tips in mind:
- Be Prepared: Bring all relevant medical information to your first appointment with your new doctor.
- Communicate Clearly: Clearly communicate your health history, concerns, and goals to your new doctor.
- Ask Questions: Do not hesitate to ask questions and seek clarification on anything you do not understand.
- Be Open-Minded: Give your new doctor a chance to get to know you and your health needs.
- Follow Recommendations: Follow their recommendations and treatment plan.
- Schedule Regular Check-Ups: Schedule regular check-ups to maintain your health and build a relationship with your new doctor.
These steps will help you establish a positive and productive relationship with your new healthcare provider.
9. The Importance of Continuity of Care
Continuity of care refers to the seamless coordination of healthcare services over time. It is crucial for maintaining your health and well-being.
- Comprehensive Understanding: Your doctor has a comprehensive understanding of your medical history and current health status.
- Preventative Care: It ensures you receive appropriate preventative care and screenings.
- Medication Management: It allows for effective medication management and monitoring.
- Coordination of Specialists: It facilitates coordination between specialists and other healthcare providers.
- Better Outcomes: Studies show that continuity of care leads to better health outcomes and patient satisfaction.
To ensure continuity of care, communicate openly with your doctor, keep them informed of any changes in your health, and follow their recommendations.
10. How to Evaluate Your New Doctor After the First Few Visits
After a few visits with your new doctor, take time to evaluate whether they are the right fit for you.
- Communication: Are they a good communicator who listens to your concerns?
- Trust: Do you trust their medical advice and recommendations?
- Comfort Level: Do you feel comfortable discussing sensitive health issues with them?
- Professionalism: Are they professional, respectful, and attentive?
- Effectiveness: Are their treatments effective in addressing your health issues?
- Accessibility: Are they accessible and responsive to your needs?
- Overall Satisfaction: Are you satisfied with the overall experience of being their patient?
If you answered no to several of these questions, it might be time to consider finding another doctor.
11. Common Foot Problems That May Require a Podiatrist
Foot problems can significantly impact your quality of life. Here are some common issues that may require a podiatrist:
- Plantar Fasciitis: Inflammation of the plantar fascia, causing heel pain.
- Bunions: Bony bumps that form on the joint at the base of the big toe.
- Hammertoes: Deformities of the toes, causing them to bend abnormally.
- Ingrown Toenails: Toenails that grow into the surrounding skin.
- Athlete’s Foot: A fungal infection that causes itching, burning, and scaling.
- Diabetic Foot Ulcers: Open sores that develop on the feet of people with diabetes.
- Neuromas: Thickening of nerve tissue in the foot, causing pain and numbness.
- Ankle Sprains: Injuries to the ligaments that support the ankle.
- Flat Feet: A condition in which the arch of the foot collapses.
- Heel Spurs: Bony growths that form on the heel bone.
These conditions can often be effectively treated by a podiatrist.
12. Preventative Foot Care Tips
Preventative foot care is essential for maintaining healthy feet and preventing problems.
- Wear Proper Shoes: Wear shoes that fit well and provide adequate support.
- Keep Feet Clean and Dry: Wash your feet daily and dry them thoroughly, especially between the toes.
- Trim Toenails Properly: Trim your toenails straight across to prevent ingrown toenails.
- Moisturize Feet: Apply moisturizer to your feet to prevent dry, cracked skin.
- Inspect Feet Regularly: Regularly inspect your feet for any signs of problems, such as cuts, blisters, or infections.
- Wear Socks Made of Breathable Materials: Choose socks made of breathable materials like cotton or wool to keep your feet dry.
- Avoid Walking Barefoot in Public Places: Avoid walking barefoot in public places to prevent fungal infections.
- Stretch Your Feet and Ankles: Regularly stretch your feet and ankles to improve flexibility and prevent injuries.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to keep your skin hydrated.
- See a Podiatrist Regularly: Schedule regular check-ups with a podiatrist for professional foot care.
Following these tips can help you maintain healthy feet and prevent foot problems.
13. The Role of thebootdoctor.net in Your Foot Health Journey
thebootdoctor.net is your trusted resource for all things related to foot health.
- Expert Advice: We provide expert advice from experienced podiatrists and healthcare professionals.
- Comprehensive Information: We offer comprehensive information on various foot conditions, treatments, and preventative measures.
- Product Recommendations: We recommend high-quality products and services to support your foot health.
- Latest Research: We stay up-to-date on the latest research and advancements in podiatric care.
- Community Support: We provide a supportive community where you can connect with others and share your experiences.
Visit thebootdoctor.net today to explore our resources and take control of your foot health.
14. Understanding the Importance of Podiatric Care
Podiatric care is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. The feet are the foundation of the body, and problems with your feet can lead to pain, discomfort, and mobility issues. According to a study by the APMA, approximately 75% of Americans will experience foot problems at some point in their lives. Podiatrists are doctors who specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of foot and ankle conditions. They can provide a wide range of services, including:
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Foot and Ankle Conditions: Podiatrists can diagnose and treat a variety of foot and ankle conditions, such as plantar fasciitis, bunions, hammertoes, ingrown toenails, and ankle sprains.
- Surgical Procedures: They can perform surgical procedures to correct foot and ankle deformities or injuries.
- Custom Orthotics: Podiatrists can prescribe custom orthotics to provide support and cushioning for your feet.
- Diabetic Foot Care: They can provide specialized care for people with diabetes to prevent foot ulcers and other complications.
- Sports Medicine: Podiatrists can help athletes prevent and treat foot and ankle injuries.
- Pediatric Foot Care: They can provide care for children with foot and ankle problems.
Seeing a podiatrist regularly can help you maintain healthy feet and prevent serious complications.
15. Advanced Treatments in Podiatry
Podiatry has advanced significantly in recent years, with new technologies and techniques improving patient outcomes. Some of the advanced treatments available include:
- Laser Therapy: Used to treat fungal infections, plantar fasciitis, and other conditions.
- Minimally Invasive Surgery: Techniques that involve smaller incisions, leading to less pain and faster recovery.
- Regenerative Medicine: Using techniques like platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections to promote healing.
- Advanced Imaging: Using advanced imaging techniques like MRI and CT scans to diagnose foot and ankle conditions accurately.
- Computer-Aided Design and Manufacturing (CAD/CAM) Orthotics: Creating custom orthotics using computer technology for a precise fit.
- Nerve Decompression Surgery: Relieving pressure on nerves in the foot and ankle to treat conditions like neuromas.
- Total Ankle Replacement: Replacing damaged ankle joints with artificial joints to relieve pain and improve mobility.
These advancements have revolutionized podiatric care and offer new hope for people with chronic foot and ankle problems.
16. Understanding Common Foot Deformities
Foot deformities can affect people of all ages and can cause pain, discomfort, and mobility issues. Some common foot deformities include:
- Bunions: Bony bumps that form on the joint at the base of the big toe.
- Hammertoes: Deformities of the toes, causing them to bend abnormally.
- Claw Toes: Toes that are bent into a claw-like shape.
- Mallet Toes: Toes that are bent at the joint closest to the toenail.
- Flat Feet: A condition in which the arch of the foot collapses.
- High Arches: A condition in which the arch of the foot is excessively high.
- Clubfoot: A congenital deformity in which the foot is twisted inward and downward.
These deformities can be caused by genetics, injury, or underlying medical conditions.
17. The Link Between Foot Health and Overall Well-being
Foot health is closely linked to overall well-being. Problems with your feet can affect your ability to walk, stand, and participate in daily activities. This can lead to pain, discomfort, and a reduced quality of life. Additionally, foot problems can be a sign of underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes, arthritis, and circulatory problems.
- Mobility: Healthy feet are essential for mobility and independence.
- Pain Management: Foot pain can be debilitating and can affect your ability to work, exercise, and socialize.
- Early Detection of Medical Conditions: Foot problems can be an early sign of underlying medical conditions, allowing for prompt diagnosis and treatment.
- Improved Quality of Life: Maintaining healthy feet can improve your quality of life and allow you to enjoy a more active and fulfilling lifestyle.
Taking care of your feet is an investment in your overall health and well-being.
18. How Diabetes Affects Foot Health
Diabetes can have a significant impact on foot health. People with diabetes are at increased risk of developing foot problems due to nerve damage (neuropathy) and poor circulation. Neuropathy can cause a loss of sensation in the feet, making it difficult to detect injuries or infections. Poor circulation can slow down healing and increase the risk of complications.
- Diabetic Neuropathy: Nerve damage that can cause a loss of sensation in the feet.
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): Reduced blood flow to the feet.
- Diabetic Foot Ulcers: Open sores that develop on the feet due to nerve damage and poor circulation.
- Infections: Increased risk of infections due to impaired immune function.
- Amputation: In severe cases, diabetes can lead to amputation of the toes, feet, or legs.
People with diabetes need to take extra care of their feet to prevent complications. This includes:
- Daily Foot Inspections: Inspecting your feet daily for any signs of cuts, blisters, or infections.
- Proper Foot Hygiene: Washing your feet daily and drying them thoroughly, especially between the toes.
- Wearing Proper Shoes: Wearing shoes that fit well and provide adequate support.
- Avoiding Walking Barefoot: Avoiding walking barefoot to prevent injuries.
- Regular Check-Ups with a Podiatrist: Seeing a podiatrist regularly for professional foot care.
19. Choosing the Right Footwear
Choosing the right footwear is essential for maintaining healthy feet. The right shoes can provide support, cushioning, and protection, while the wrong shoes can cause pain, discomfort, and foot problems.
- Proper Fit: Choose shoes that fit well and provide adequate room for your toes.
- Arch Support: Look for shoes with good arch support to help distribute weight evenly across your feet.
- Cushioning: Choose shoes with cushioning to absorb shock and reduce pressure on your feet.
- Breathable Materials: Look for shoes made of breathable materials to keep your feet dry and prevent fungal infections.
- Activity-Specific Shoes: Choose shoes that are designed for your specific activities, such as running shoes for running or hiking boots for hiking.
- Avoid High Heels: Limit your use of high heels, as they can put excessive pressure on your feet and cause foot problems.
Consult with a podiatrist or shoe professional for personalized recommendations on the best footwear for your needs.
20. Exercises for Healthy Feet
Regular exercise can help keep your feet strong and flexible. Here are some simple exercises you can do at home:
- Toe Curls: Curl your toes inward and hold for a few seconds.
- Toe Raises: Raise your toes off the ground while keeping your heels on the ground.
- Heel Raises: Raise your heels off the ground while keeping your toes on the ground.
- Ankle Rotations: Rotate your ankles in a circular motion.
- Marble Pick-Ups: Pick up marbles with your toes and place them in a bowl.
- Towel Curls: Place a towel on the floor and curl it towards you with your toes.
- Calf Stretches: Stretch your calf muscles by leaning against a wall with one leg extended behind you.
These exercises can help improve flexibility, strength, and circulation in your feet.
21. Understanding Foot Pain
Foot pain is a common problem that can be caused by a variety of factors. Some common causes of foot pain include:
- Plantar Fasciitis: Inflammation of the plantar fascia, causing heel pain.
- Bunions: Bony bumps that form on the joint at the base of the big toe.
- Hammertoes: Deformities of the toes, causing them to bend abnormally.
- Ingrown Toenails: Toenails that grow into the surrounding skin.
- Athlete’s Foot: A fungal infection that causes itching, burning, and scaling.
- Ankle Sprains: Injuries to the ligaments that support the ankle.
- Fractures: Breaks in the bones of the foot or ankle.
- Arthritis: Inflammation of the joints in the foot or ankle.
- Nerve Damage: Damage to the nerves in the foot, causing pain, numbness, or tingling.
If you are experiencing foot pain, it is essential to see a doctor to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment.
22. The Future of Podiatric Care
The future of podiatric care is bright, with new technologies and treatments constantly being developed. Some trends to watch for include:
- Telemedicine: Using technology to provide remote consultations and care.
- 3D Printing: Creating custom orthotics and prosthetics using 3D printing technology.
- Robotics: Using robots to assist with surgical procedures.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Using AI to diagnose and treat foot and ankle conditions.
- Personalized Medicine: Tailoring treatments to the individual needs of each patient.
- Regenerative Medicine: Developing new ways to regenerate damaged tissues in the foot and ankle.
These advancements have the potential to transform podiatric care and improve the lives of people with foot and ankle problems.
23. The Importance of Early Intervention
Early intervention is crucial for preventing foot problems from becoming more severe. Many foot conditions can be effectively treated with conservative measures if they are diagnosed early.
- Preventing Complications: Early treatment can prevent complications such as infections, deformities, and chronic pain.
- Improving Outcomes: Early intervention can improve treatment outcomes and reduce the need for more invasive procedures.
- Reducing Costs: Early treatment can reduce healthcare costs by preventing the need for more expensive treatments later on.
- Improving Quality of Life: Early intervention can improve your quality of life by relieving pain and restoring mobility.
If you are experiencing any foot problems, see a podiatrist as soon as possible to receive a diagnosis and treatment plan.
24. Addressing Common Misconceptions About Foot Health
There are many misconceptions about foot health that can lead to poor foot care practices. Some common misconceptions include:
- “Foot pain is normal and nothing to worry about.” Foot pain is not normal and can be a sign of an underlying problem.
- “You can treat foot problems at home without seeing a doctor.” Some foot problems require professional treatment.
- “All shoes are created equal.” The wrong shoes can cause foot problems.
- “Surgery is the only option for treating foot problems.” Many foot problems can be treated with conservative measures.
- “Podiatrists only treat minor foot problems.” Podiatrists can treat a wide range of foot and ankle conditions, including complex problems.
It is essential to get accurate information about foot health from reliable sources, such as thebootdoctor.net and your podiatrist.
25. Benefits of Consulting a Podiatrist
Consulting a podiatrist offers numerous benefits for your foot health. Podiatrists are highly trained medical professionals who specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of foot and ankle conditions.
- Expert Diagnosis: Podiatrists can accurately diagnose the cause of your foot pain and other symptoms.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: They can develop personalized treatment plans to address your specific needs.
- Advanced Treatments: Podiatrists have access to advanced treatments and technologies to provide the best possible care.
- Preventative Care: They can provide preventative care to help you maintain healthy feet and prevent problems.
- Improved Quality of Life: Podiatrists can help you relieve pain, improve mobility, and enhance your overall quality of life.
If you are experiencing any foot problems, consulting a podiatrist is the best way to get the care you need.
26. Insurance Coverage for Podiatric Services
Many insurance plans cover podiatric services, but coverage can vary depending on your plan.
- Check Your Policy: Review your insurance policy to understand the extent of your coverage for podiatric services.
- In-Network vs. Out-of-Network: Determine whether your podiatrist is in your insurance network.
- Referrals: Find out if your plan requires a referral from your primary care physician to see a podiatrist.
- Co-pays and Deductibles: Be aware of your co-pay and deductible amounts for podiatric visits.
- Pre-authorization: Check if your plan requires pre-authorization for certain podiatric procedures.
Contact your insurance company or your podiatrist’s office for assistance with understanding your coverage.
27. The Importance of Foot Care for Seniors
Foot care is particularly important for seniors, who are at increased risk of developing foot problems due to age-related changes, medical conditions, and mobility issues.
- Age-Related Changes: The feet can undergo age-related changes, such as loss of elasticity, thinning of the skin, and decreased cushioning.
- Medical Conditions: Seniors are more likely to have medical conditions that can affect the feet, such as diabetes, arthritis, and circulatory problems.
- Mobility Issues: Foot problems can contribute to mobility issues and increase the risk of falls.
- Preventing Complications: Proper foot care can help prevent complications such as infections, ulcers, and amputations.
Seniors should inspect their feet daily, wear proper shoes, and see a podiatrist regularly for professional foot care.
28. The Connection Between Foot Health and Mental Well-being
Foot health is closely connected to mental well-being. Chronic foot pain and mobility issues can lead to depression, anxiety, and social isolation.
- Physical Activity: Foot pain can limit your ability to engage in physical activity, which is essential for mental health.
- Social Interaction: Foot problems can make it difficult to socialize and participate in social activities.
- Self-Esteem: Foot deformities and other foot problems can affect your self-esteem and body image.
- Stress: Chronic foot pain can lead to increased stress levels.
Taking care of your feet can improve your mental well-being and help you live a happier, more fulfilling life.
29. The Impact of Foot Health on Athletic Performance
Foot health is critical for athletic performance. Your feet are the foundation of your body, and problems with your feet can affect your balance, stability, and power.
- Balance and Stability: Healthy feet provide a stable base for athletic movements.
- Power and Agility: Strong, flexible feet can enhance power and agility.
- Injury Prevention: Proper foot care can help prevent foot and ankle injuries.
- Performance Enhancement: Optimal foot health can improve athletic performance.
Athletes should wear shoes that are designed for their specific sport and consult with a podiatrist to address any foot problems.
30. Foot Care During Pregnancy
Pregnancy can cause significant changes in the feet due to hormonal shifts, weight gain, and fluid retention.
- Swelling: Swelling in the feet and ankles is common during pregnancy.
- Arch Support: The arches of the feet can flatten due to increased weight.
- Shoe Size: Shoe size may increase during pregnancy.
- Plantar Fasciitis: Pregnant women are at increased risk of developing plantar fasciitis.
- Varicose Veins: Pregnancy can worsen varicose veins in the legs and feet.
Pregnant women should wear comfortable shoes with good arch support, elevate their feet when possible, and stay hydrated.
31. How to Choose the Right Socks
Choosing the right socks is essential for maintaining healthy feet.
- Material: Choose socks made of breathable materials like cotton, wool, or synthetic fabrics.
- Fit: Make sure your socks fit well and are not too tight or too loose.
- Cushioning: Look for socks with cushioning to provide extra comfort and protection.
- Moisture-Wicking: Choose socks that wick away moisture to keep your feet dry.
- Seamless: Look for socks with seamless construction to prevent friction and blisters.
Avoid wearing socks that are too tight, as they can restrict circulation.
32. Addressing Foot Odor
Foot odor is a common problem caused by bacteria that thrive in warm, moist environments.
- Proper Hygiene: Wash your feet daily with soap and water and dry them thoroughly.
- Breathable Shoes: Wear shoes made of breathable materials.
- Change Socks Daily: Change your socks daily and more often if your feet sweat excessively.
- Antiperspirants: Use an antiperspirant on your feet to reduce sweating.
- Foot Soaks: Soak your feet in a solution of water and Epsom salts to kill bacteria.
- Odor-Absorbing Insoles: Use odor-absorbing insoles in your shoes.
If foot odor persists, see a doctor to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
33. Managing Corns and Calluses
Corns and calluses are thickened areas of skin that develop in response to pressure or friction.
- Proper Shoes: Wear shoes that fit well and provide adequate cushioning.
- Padding: Use padding to protect corns and calluses from pressure.
- Soaking: Soak your feet in warm water to soften corns and calluses.
- Exfoliation: Gently exfoliate corns and calluses with a pumice stone or foot file.
- Moisturizing: Apply moisturizer to your feet to keep the skin soft.
Avoid cutting or shaving corns and calluses, as this can lead to infection.
34. Understanding Plantar Warts
Plantar warts are warts that develop on the soles of the feet.
- Contagious: Plantar warts are contagious and can spread through direct contact.
- Appearance: They often appear as small, rough growths with black dots.
- Treatment: Plantar warts can be treated with over-the-counter medications, prescription medications, or procedures performed by a doctor.
- Prevention: Avoid walking barefoot in public places and keep your feet clean and dry to prevent plantar warts.
If you suspect you have a plantar wart, see a doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
35. How to Find a Doctor Who Listens
Finding a doctor who listens is essential for receiving quality healthcare.
- Ask for Recommendations: Seek recommendations from friends, family, or colleagues.
- Read Reviews: Check online reviews to see what other patients have to say about a doctor’s communication skills.
- Schedule a Consultation: Schedule a consultation with a potential new doctor to assess their communication style.
- Ask Questions: Ask questions and express your concerns during the consultation.
- Observe Body Language: Pay attention to the doctor’s body language and attentiveness.
If you feel that a doctor is not listening to your concerns, consider finding another doctor who is a better fit for you.
36. Navigating the Healthcare System
Navigating the healthcare system can be challenging.
- Understand Your Insurance: Know your insurance coverage and how to access care.
- Find a Primary Care Physician: Establish a relationship with a primary care physician.
- Utilize Online Resources: Use online resources to find doctors, research medical conditions, and access healthcare information.
- Ask Questions: Don’t hesitate to ask questions and seek clarification from healthcare providers.
- Keep Records: Maintain accurate records of your medical history, medications, and treatments.
The thebootdoctor.net is here to support you and provide information to guide you in the right direction.
37. Resources for Foot Health Information
There are many resources available for foot health information.
- thebootdoctor.net: Your trusted source for expert advice and comprehensive information on foot health.
- American Podiatric Medical Association (APMA): A professional organization for podiatrists.
- National Institutes of Health (NIH): A government agency that conducts medical research.
- Mayo Clinic: A non-profit medical center that provides information on various medical conditions.
Use these resources to stay informed about foot health and make informed decisions about your care.
38. Addressing the Fear of Changing Doctors
Changing doctors can be a daunting decision, and it is normal to feel apprehensive.
- Acknowledge Your Feelings: Acknowledge your fears and anxieties about changing doctors.
- Focus on Your Needs: Focus on your healthcare needs and what you are looking for in a doctor.
- Do Your Research: Research potential new doctors and gather information to make an informed decision.
- Seek Support: Talk to friends, family, or a therapist to gain support and reassurance.
- Take It One Step at a Time: Take the process one step at a time and don’t feel pressured to make a decision immediately.
Remember that changing doctors is a personal decision, and you have the right to choose the healthcare provider who is the best fit for you.
FAQ About Changing Doctors
1. How often can I change my doctor?
You can generally change your doctor as often as you need, but check with your insurance plan for any specific rules or restrictions.
2. Will my insurance cover a visit to a new doctor?
Yes, as long as the doctor is in your insurance network. Check with your insurance provider to confirm coverage.
3. How do I transfer my medical records to a new doctor?
Contact your old doctor’s office and request a medical records release form. Fill it out and specify the new doctor’s information.
4. What if I don’t like my new doctor after the first visit?
It’s okay to seek another doctor if you’re not satisfied. Trust your instincts and find someone who meets your needs.
5. Do I need to tell my old doctor that I’m leaving?
It’s a professional courtesy, but not required. It can also provide valuable feedback for their practice.
6. What should I bring to my first appointment with a new doctor?
Bring your insurance card, a list of medications, and any relevant medical history information.
7. How can I find a doctor who specializes in foot problems?
Search for a podiatrist in your area through the APMA website or online directories like Healthgrades.
8. What if my doctor leaves their practice?
The practice may assign you to a new doctor, or you’ll need to find a new healthcare provider and request your records.
9. Can changing doctors affect my prescriptions?
Yes, you’ll need to have your prescriptions transferred or re-written by your new doctor.
10. Is it better to see a doctor who is affiliated with a hospital?
It can be beneficial, as it often indicates access to more resources and specialists.
Changing doctors is a significant step in managing your healthcare. We hope this comprehensive guide has equipped you with the knowledge and confidence to make informed decisions. For more expert advice and resources on foot health, visit thebootdoctor.net. Your feet will thank you. If you’re in the Houston area and looking for exceptional foot care, visit us at 6565 Fannin St, Houston, TX 77030, United States, or