Are Doctors In Debt? Yes, many doctors face significant debt due to the high costs of medical education, but understanding the facts can help you navigate your financial future, and thebootdoctor.net is here to help you explore the realities of medical school debt, offering insights into managing your finances and planning for a healthy financial future. Addressing student loan repayment, debt management, and financial planning in the medical profession.
1. What Is the Average Debt for Medical School Graduates?
The average debt for medical school graduates is significant. Medical school graduates often face substantial debt due to the high costs of tuition, fees, and living expenses. According to the Education Data Initiative, the average medical school debt is $243,483, including premedical debt. This financial burden can impact their career choices and financial well-being for years to come.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown:
- Total Educational Debt: Medical school graduates owe an average of $243,483, which includes premedical debt.
- Medical School Debt Alone: For medical school alone, the average debt is $234,597, excluding premedical undergraduate and other educational debt.
- Graduates with Premedical Debt: Medical school graduates with both medical school and premedical debt, but no non-educational debt, face an average of $264,519 in debt.
These figures highlight the considerable financial investment required to become a doctor, impacting not only their early careers but also their long-term financial planning.
2. What Percentage of Medical School Graduates Have Debt?
A significant percentage of medical school graduates have educational debt. According to recent statistics, about 73% of medical school graduates carry educational debt. This high percentage underscores the financial challenges faced by the majority of aspiring doctors.
To break it down further:
- Graduates with Debt: 73% of medical school graduates have educational debt.
- Premedical Debt: 31% of indebted medical school graduates also have premedical educational debt.
These numbers indicate that most medical school graduates rely on loans to finance their education, which can significantly affect their financial decisions post-graduation.
3. How Does Medical School Debt Compare to Other Postgraduate Debt?
Medical school debt is notably higher than other postgraduate debt. The average medical school graduate owes 2.25 times as much as the average postgraduate college student, including their undergraduate debt. This significant difference highlights the unique financial challenges faced by medical professionals.
Here’s a comparison to provide context:
- Medical School vs. Postgraduate: Medical school graduates owe 2.25 times more than the average postgraduate student.
- Loan Usage: 70% of medical school students use loans specifically to help pay for medical school, as opposed to undergraduate or premed debt.
The higher debt burden for medical students is due to the longer duration and higher costs associated with medical education, requiring more substantial financial planning and management.
 Medical student loan debt statistics
Medical student loan debt statistics
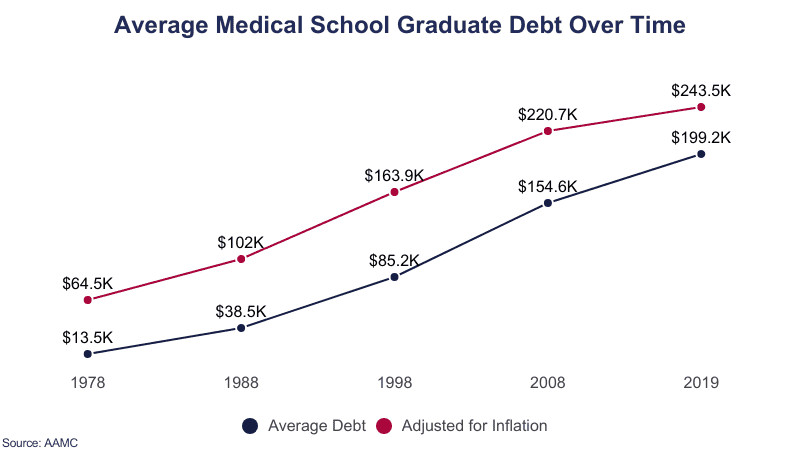
4. How Has Medical School Debt Changed Over Time?
Medical school debt has significantly increased over time. The average debt has risen dramatically, outpacing both academic and economic inflation. This trend poses considerable challenges for current and future medical professionals.
Here’s a look at how debt has evolved:
- 1978: The average medical school debt was $13,500, which is equivalent to $64,534 in 2024.
- 1999-2000: The average total student loan debt was $87,020, equivalent to $162,390 in 2024.
- 2016: The average medical school debt was $223,060, equivalent to $291,139 in 2024.
- Growth Rate: Average debt increased by 48.5% between 1998 and 2019.
These figures demonstrate the increasing financial strain on medical students, making it essential to understand debt management and repayment options.
5. What Factors Contribute to the High Cost of Medical School?
Several factors contribute to the high cost of medical school. These include rising tuition fees, increased living expenses, and the extended duration of medical education. Understanding these factors can help students and policymakers address the financial challenges in medical education.
Key factors include:
- Tuition and Fees: The average cost of tuition and fees for a first-year medical student in the 2023-2024 school year was $58,327.
- Historical Increase: The cost of medical school increased 39% in 23 years after adjusting for inflation.
- Application Costs: The average cost of medical school application fees in 2023 was $2,833, with an application budget recommended at $10,000.
These costs underscore the need for comprehensive financial planning and exploring various funding and repayment options to mitigate the financial burden.
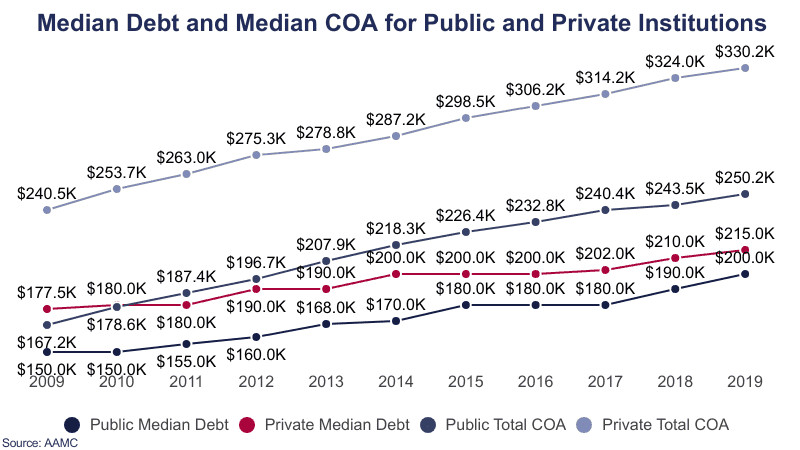
6. How Does Debt Differ Between Public and Private Medical Schools?
Debt levels differ between public and private medical schools. Graduates from private medical schools typically owe more than those from public institutions. This difference is primarily due to the higher tuition fees associated with private schools.
Here’s a comparison:
- Debt Difference: Public medical school graduates owed $15,000 less on average than private medical school graduates.
- Median Debt (Private): The median student debt among private medical school graduates in 2016 was $200,000, while the median cost of private in-state medical school was $306,171.
- Median Debt (Public): The median student debt among public medical school graduates in 2016 was $180,000, while the median cost of public in-state medical school was $232,838.
Choosing between a public and private medical school can significantly impact the total debt burden, making it a crucial consideration during the application process.
7. What Are the Available Loan Repayment Programs for Doctors?
Various loan repayment programs are available for doctors. These programs aim to alleviate the financial burden by offering options such as income-driven repayment plans and loan forgiveness programs. Understanding these options is essential for managing medical school debt effectively.
Key programs include:
- Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF): For physicians entering non-profit or government agencies, the full loan balance can be forgiven after 10 years of repayments, reducing total repayments to around $135,000, including interest.
- Income-Driven Repayment Plans: These plans base monthly payments on income and family size, offering more affordable payment options.
These programs can significantly ease the financial strain on doctors, allowing them to focus on their careers and personal finances.
8. How Do Interest Rates Affect Medical School Loan Repayments?
Interest rates significantly affect medical school loan repayments. High interest rates can substantially increase the total amount repaid over the life of the loan. Understanding the impact of interest rates is crucial for making informed decisions about loan repayment strategies.
Here’s how interest impacts repayments:
- Interest Payments: Interest payments alone can account for $164,000 – $254,000 of repayments on a $200,000 loan.
- Fixed Interest Rate Example: At a fixed interest rate of 8.08%, borrowers with $200,000 in federal student loan debt would be required to pay $2,435 in monthly payments to pay off all educational debts within 10 years. The total payment would amount to $292,202, of which $92,202 is interest.
Managing interest rates through refinancing or choosing appropriate repayment plans can save doctors a significant amount of money over time.
9. How Does Medical School Debt Impact Different Demographics?
Medical school debt impacts different demographics unevenly. Certain racial and ethnic groups, as well as students from low-income families, often face higher debt burdens. Understanding these disparities is essential for addressing systemic inequalities in medical education.
Here’s a look at debt demographics:
- Black Non-Hispanic Students: Carry more debt than any other race or ethnicity, with 91% having debt, compared to the 72% average across all students. Their median educational debt is also significantly higher at $230,000, compared to the median of $200,000 for all students.
- Asian Non-Hispanic Students: Have the lowest proportion of graduates carrying debt at 61%, and the lowest median education debt balance at $180,000.
- Low-Income Families: The median education debt of students from low-income families was $212,000, larger than any other income category.
Addressing these disparities requires targeted support and financial aid programs to ensure equitable access to medical education.
10. What Are the Socioeconomic Factors Influencing Medical School Debt?
Socioeconomic factors significantly influence medical school debt. Students from wealthier families are more likely to attend medical school, while low-income students are attending at decreasing rates, possibly due to the fear of debt. These trends highlight the importance of financial support for aspiring doctors from disadvantaged backgrounds.
Key socioeconomic factors include:
- Ability to Pay Off Debt: 48.2% of medical school students entering in 2023 cite their ability to pay off debt as a primary concern.
- Low-Income Students: The proportion of low-income students commencing medical school has been steadily dropping since 2017, dropping by 1.3%.
Creating more equitable pathways to medical education requires comprehensive financial aid, scholarships, and loan forgiveness programs to support students from all socioeconomic backgrounds.
11. What Strategies Can Medical Students Use to Minimize Debt?
Medical students can use several strategies to minimize debt. These include applying for scholarships and grants, choosing a public medical school, and managing expenses carefully. Implementing these strategies can help reduce the overall debt burden.
Here are some effective strategies:
- Apply for Scholarships and Grants: Seek out and apply for all available scholarships and grants to reduce the need for loans.
- Choose Public Medical School: Opt for a public medical school to take advantage of lower tuition fees.
- Manage Expenses: Create a budget and carefully manage living expenses to avoid unnecessary borrowing.
By proactively managing their finances, medical students can minimize debt and set themselves up for a more secure financial future.
12. How Does the Cost of Living Affect Medical School Debt?
The cost of living significantly affects medical school debt. High living expenses can force students to borrow more money, increasing their overall debt burden. Managing these costs is essential for controlling debt levels.
Here’s how cost of living impacts debt:
- Increased Borrowing: High living expenses lead to increased borrowing, adding to the total debt.
- Budgeting: Effective budgeting and cost management can help reduce the need for additional loans.
Students should consider living in more affordable areas or with roommates to help manage living expenses and minimize debt.
13. Are There Loan Forgiveness Programs for Doctors in Rural Areas?
Yes, there are loan forgiveness programs for doctors in rural areas. These programs incentivize doctors to practice in underserved areas by offering loan repayment assistance. This helps address healthcare shortages in rural communities while also reducing the doctor’s debt burden.
Key programs include:
- National Health Service Corps (NHSC) Loan Repayment Program: Offers loan repayment assistance to healthcare professionals who commit to working in underserved communities.
- State-Specific Programs: Many states offer loan forgiveness programs for doctors practicing in rural or underserved areas.
These programs provide valuable opportunities for doctors to reduce their debt while providing essential healthcare services to communities in need.
14. What Role Do Medical Schools Play in Debt Management Education?
Medical schools play a crucial role in debt management education. Providing students with resources and guidance on financial planning, budgeting, and loan repayment options can help them make informed decisions and manage their debt effectively. This support is essential for ensuring the financial well-being of future doctors.
Key roles for medical schools include:
- Financial Counseling: Offering financial counseling services to help students understand their debt and repayment options.
- Workshops and Seminars: Conducting workshops and seminars on budgeting, debt management, and financial planning.
- Resource Provision: Providing access to resources and tools for managing debt effectively.
By prioritizing financial education, medical schools can empower students to make informed decisions and minimize the long-term impact of medical school debt.
15. How Can Doctors Refinance Their Medical School Loans?
Doctors can refinance their medical school loans to secure lower interest rates or more favorable repayment terms. Refinancing can potentially save thousands of dollars over the life of the loan and make monthly payments more manageable.
Here’s how refinancing works:
- Lower Interest Rates: Refinancing to a lower interest rate can significantly reduce the total amount repaid.
- Improved Terms: Refinancing can allow doctors to switch to a different repayment term, such as a shorter term to pay off the loan faster or a longer term to reduce monthly payments.
Carefully evaluating refinancing options and comparing offers from different lenders can help doctors find the best solution for their financial situation.
16. What Are the Tax Implications of Medical School Loan Repayment?
The tax implications of medical school loan repayment can be complex. Understanding these implications is crucial for making informed financial decisions and maximizing tax benefits.
Key tax considerations include:
- Student Loan Interest Deduction: Borrowers may be able to deduct student loan interest paid during the year, up to a certain limit.
- Taxability of Loan Forgiveness: In some cases, loan forgiveness may be considered taxable income, depending on the specific program.
Consulting with a tax professional can help doctors navigate these complexities and optimize their tax strategy related to medical school loan repayment.
17. How Does Medical School Debt Affect Career Choices?
Medical school debt can significantly affect career choices. High debt levels may push doctors towards higher-paying specialties or urban areas, potentially steering them away from primary care or rural practice. This impact can exacerbate healthcare disparities and limit access to care in underserved communities.
Here’s how debt influences career decisions:
- Specialty Choice: Doctors may choose higher-paying specialties to pay off debt more quickly.
- Location: Debt can influence the decision to practice in urban areas with higher earning potential.
Addressing medical school debt is essential for ensuring that doctors can pursue their passions and serve the communities that need them most.
18. What Are the Long-Term Financial Impacts of Medical School Debt?
The long-term financial impacts of medical school debt can be substantial. High debt levels can delay major life milestones such as buying a home, starting a family, and saving for retirement. Effectively managing debt is crucial for achieving long-term financial security.
Potential long-term impacts include:
- Delayed Homeownership: High debt can make it difficult to save for a down payment on a home.
- Delayed Family Planning: Debt may delay the decision to start a family due to financial constraints.
- Reduced Retirement Savings: Debt can limit the ability to save for retirement, impacting long-term financial security.
By proactively managing their debt and making informed financial decisions, doctors can mitigate these long-term impacts and achieve their financial goals.
19. What Resources Are Available for Doctors to Manage Their Debt?
Numerous resources are available for doctors to manage their debt effectively. These resources include financial advisors, online tools, and professional organizations that offer guidance and support.
Key resources include:
- Financial Advisors: Consulting with a financial advisor can provide personalized guidance on debt management and financial planning.
- Online Tools: Utilize online calculators and budgeting tools to track expenses and assess repayment options.
- Professional Organizations: Organizations like the American Medical Association (AMA) offer resources and support for debt management.
Leveraging these resources can empower doctors to take control of their finances and achieve their financial goals.
20. How Can Thebootdoctor.Net Help Doctors With Financial Planning?
Thebootdoctor.net can assist doctors with financial planning by providing valuable information and resources tailored to their unique needs. Our platform offers expert articles, practical tips, and personalized advice to help doctors manage their debt, plan for the future, and achieve financial success.
Here’s how thebootdoctor.net supports doctors:
- Expert Financial Advice: Access articles and guides written by financial experts on topics relevant to doctors.
- Debt Management Strategies: Learn effective strategies for managing medical school debt and optimizing repayment plans.
- Financial Planning Tools: Utilize budgeting tools and calculators to track expenses and plan for financial goals.
- Community Support: Connect with a community of doctors and financial professionals to share experiences and gain insights.
By leveraging the resources available at thebootdoctor.net, doctors can gain the knowledge and tools they need to make informed financial decisions and build a secure future.
 Medical student loan debt chart
Medical student loan debt chart
FAQ: Medical School Debt
1. Is Medical School Worth The Debt?
Yes, for most doctors, medical school is worth the debt. Despite the high cost of medical education, the long-term earning potential and personal fulfillment of a medical career often outweigh the financial burden. The median salary for physicians in the United States is significantly higher than the national average, allowing them to pay off their loans and build a comfortable life. Additionally, the intellectual stimulation and the opportunity to make a positive impact on people’s lives make the investment worthwhile for many.
2. How Can I Pay Off Medical School Debt Fast?
You can pay off medical school debt fast by employing several strategies. First, consider refinancing your loans to secure a lower interest rate, which can significantly reduce the total amount you repay. Second, make extra payments whenever possible, even small amounts, to chip away at the principal. Third, explore income-driven repayment plans that allow you to pay more when your income is higher. Fourth, look into loan forgiveness programs, such as the Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) program, if you work for a qualifying non-profit or government organization.
3. What Is The Average Time To Pay Off Medical School Debt?
The average time to pay off medical school debt varies widely depending on income, lifestyle, and repayment strategies. Some doctors may pay off their loans in as little as 5 to 10 years by aggressively managing their finances. However, many others take 10 to 20 years or longer, especially if they opt for income-driven repayment plans. It’s essential to create a personalized repayment plan based on your financial situation and goals to estimate your repayment timeline accurately.
4. Are There Scholarships Or Grants To Help With Medical School Debt?
Yes, there are scholarships and grants available to help with medical school debt. The National Health Service Corps (NHSC) offers loan repayment assistance to healthcare professionals who commit to working in underserved communities. The Armed Forces also offer scholarships and loan repayment programs for doctors who serve in the military. Additionally, many medical schools and private organizations provide scholarships and grants to help students finance their education.
5. How Does Medical School Debt Impact My Mental Health?
Medical school debt can significantly impact your mental health. The stress of managing a large debt burden can lead to anxiety, depression, and burnout. It’s crucial to prioritize your mental well-being by seeking support from mental health professionals, practicing stress-reducing activities like exercise and meditation, and maintaining a healthy work-life balance. Also, connecting with peers who understand your challenges can provide valuable emotional support.
6. Can I Deduct Student Loan Interest On My Taxes?
Yes, you can deduct student loan interest on your taxes. The IRS allows you to deduct the interest you paid on qualified student loans during the tax year, up to a certain limit. This deduction can help reduce your taxable income and lower your overall tax liability. Consult with a tax professional to ensure you are taking advantage of all available tax benefits related to student loan repayment.
7. What Are The Best Budgeting Strategies For Doctors With High Debt?
The best budgeting strategies for doctors with high debt include creating a detailed budget, tracking expenses, and prioritizing debt repayment. Start by listing all your income and expenses to identify areas where you can cut back. Use budgeting apps or spreadsheets to track your spending and stay within your budget. Allocate a significant portion of your income towards debt repayment, and consider automating extra payments to stay on track. Regularly review and adjust your budget as needed to ensure it aligns with your financial goals.
8. How Do I Choose The Right Loan Repayment Plan?
Choosing the right loan repayment plan involves assessing your financial situation, career goals, and risk tolerance. Federal student loans offer several repayment options, including standard, graduated, extended, and income-driven plans. If you anticipate a high income and want to pay off your loans quickly, a standard or graduated plan may be suitable. If you have a lower income or work in public service, an income-driven repayment plan with potential loan forgiveness may be more advantageous. Carefully compare the terms, interest rates, and long-term costs of each plan before making a decision.
9. What Are The Pros And Cons Of Loan Consolidation?
Loan consolidation involves combining multiple federal student loans into a single loan with a fixed interest rate. The pros of loan consolidation include simplifying your repayment by having only one monthly payment and potentially qualifying for certain loan forgiveness programs. However, the cons include potentially losing benefits associated with your original loans, such as interest rate discounts or loan cancellation options. Additionally, consolidation may extend your repayment term, resulting in higher total interest paid over time.
10. How Can I Negotiate A Better Salary To Help Pay Off Debt?
You can negotiate a better salary to help pay off debt by researching industry standards, highlighting your unique skills and qualifications, and presenting a compelling case for your value to the employer. Before the negotiation, gather data on the average salaries for your specialty and experience level in your geographic area. During the negotiation, emphasize your strengths, accomplishments, and contributions to the organization. Be confident, professional, and willing to walk away if the offer does not meet your needs.
 Medical school debt statistics graph
Medical school debt statistics graph
Navigating medical school debt is a challenge, but with the right knowledge and strategies, doctors can achieve financial stability and success. At thebootdoctor.net, we’re committed to providing you with the resources and support you need to manage your debt and build a brighter future. Explore our website for more valuable information, articles, and tools to help you on your financial journey.
Do you have questions about medical school debt? Are you looking for personalized advice on managing your finances? Contact us today or visit thebootdoctor.net to learn more and take control of your financial future.
